How to connect two docker instances
Mar. 12, 2022This is one of the issue I see beginners struggle with. So I am just going to explain how to make two docker containers talk to each other.
There are essentially two methods:
- Make both containers in same docker network
- Expose the port to the host machine and connect using the host machine on same port
Let’s elaborate the two cases. For both cases, I will include docker-compose way and docker-cli way.
1. Make both containers in same docker network:
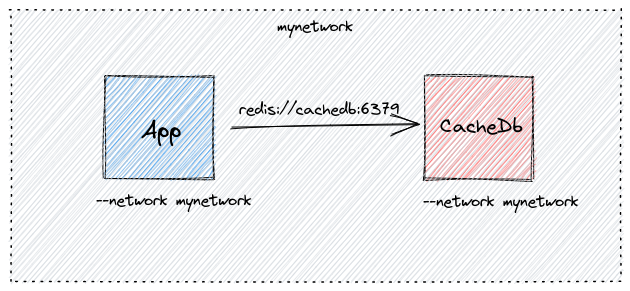
This is straight forward way to do it. All you have to do it create a docker network and assign the network to both the containers.
1.1 docker-compose way
We will consider connecting a database to an app service. For this, you will generally have docker-compose to manage them both easily.
Let’s say you have the initial version as follows.
version: '3'
services:
cachedb:
image: redis:latest
volumes:
- ./app:/app
app:
image: myapp:latest
Here, cachedb is the redis database. app is our server.
After adding docker network:
version: '3'
services:
cachedb:
image: redis:latest
volumes:
- ./app:/app
networks:
- mynetwork
app:
image: myapp:latest
networks:
- mynetwork
networks:
mynetwork:
driver: bridge
Notice, we have defined a bridge network and called it mynetwork. And then, assigned it to both docker services.
1.2 Docker CLI version
docker network create mynetwork
docker run --network=mynetwork --name cachedb -d redis
docker run --network=mynetwork --name app -d myapp
Since both the containers share the same docker network, to connect the app to the cachedb we will refer the redis instance with the alias name and docker will be able to resolve the alias name to the IP address of the container.
For example to connect the redis instance, we will use the following:
REDIS_URL = "redis://cachedb:6379"
Note: instead of
localhostwe are instead referring it by the alias name. This means you don’t need to worry about keeping track of containers’ IP addresses, which can frequently change.
2. Through the host machine
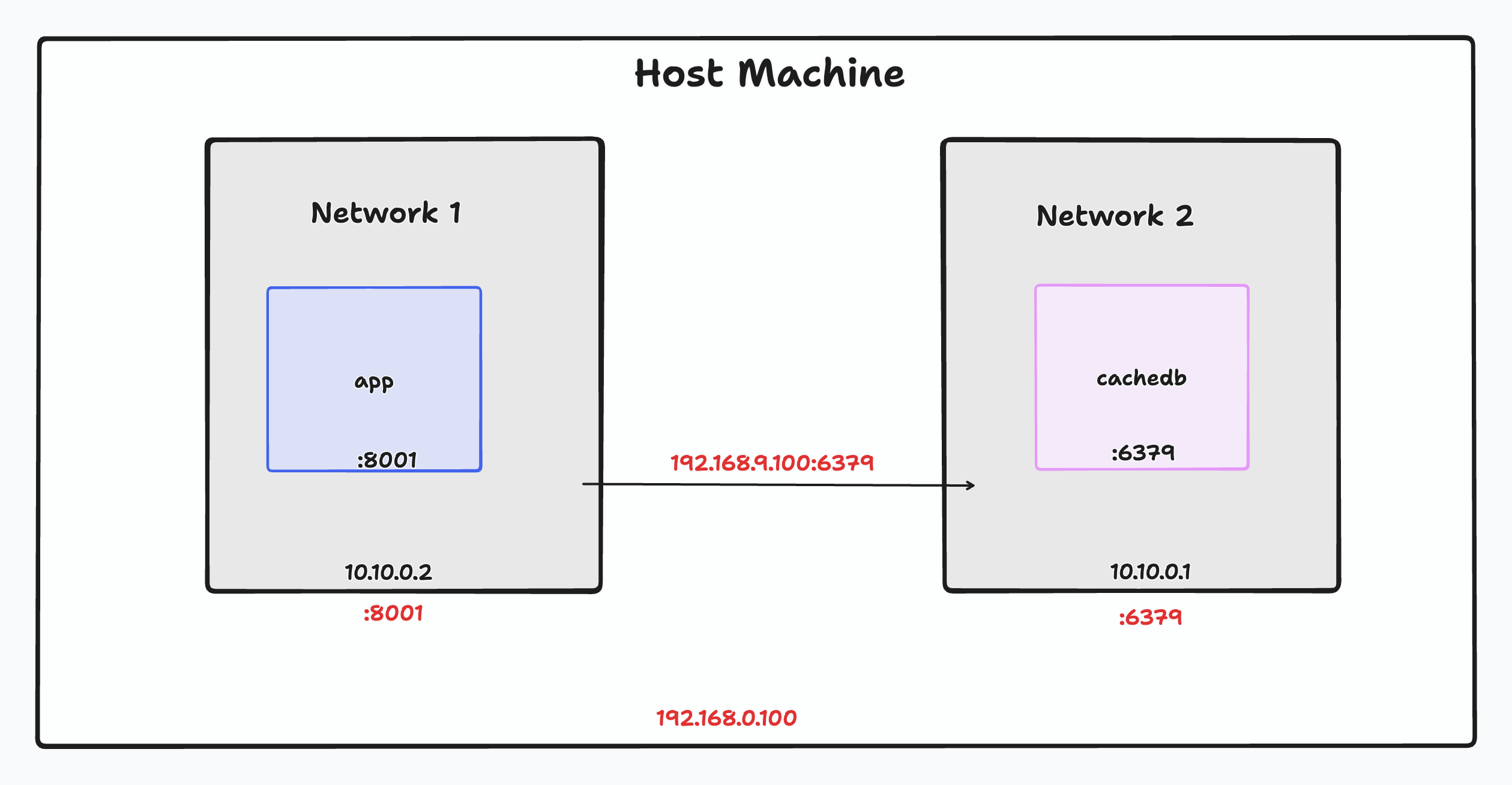 Know that the above mentioned method of getting the containers in the same network is the ideal way to connect two containers. But if you want to connect two containers in different networks, you can do it by exposing the port to the host machine and then connecting to the host machine.
Know that the above mentioned method of getting the containers in the same network is the ideal way to connect two containers. But if you want to connect two containers in different networks, you can do it by exposing the port to the host machine and then connecting to the host machine.
Step 1: Grab the IP address of the host machine using one of the following commands.
# For systems with ifconfig
ifconfig | grep -Eo 'inet (addr:)?([0-9]*\.){3}[0-9]*' | grep -Eo '([0-9]*\.){3}[0-9]*' | grep -v '127.0.0.1'
# For systems with ip command
ip addr | grep -Eo 'inet (addr:)?([0-9]*\.){3}[0-9]*' | grep -Eo '([0-9]*\.){3}[0-9]*' | grep -v '127.0.0.1'
Alternatively, on many Docker setups, you can use the special hostname host.docker.internal to refer to the host machine from within a container.
Step 2: Run the redis container while exposing the port to the host machine.
docker run -d -p 6379:6379 redis
Step 3: Since the redis instance is running on the host machine, we can connect to it using the host machine IP address.
docker run -p 8001:8001 --env REDIS_URL="redis://<HostIP>:6379" myapp
If your Docker setup supports it, you can also use:
docker run -p 8001:8001 --env REDIS_URL="redis://host.docker.internal:6379" myapp
This is how you can connect two docker containers. I hope this helps you.